Ensuring Business Continuity: A Guide to Choosing the Right Disaster Recovery Strategy on AWS
In today's digital landscape, ensuring the availability and resilience of our systems and applications is of utmost importance. Unforeseen events such as natural disasters, hardware failures, or human errors can hurt business continuity and lead to significant downtime, data loss, and financial loss. That's where having a robust disaster recovery strategy becomes crucial. In this article, we will explore the various considerations and options available for implementing a disaster recovery plan for your solutions built on AWS. We'll delve into the key factors to consider, different recovery strategies, and how AWS provides a comprehensive suite of tools and services to help you design a resilient and fault-tolerant architecture. Whether you're running critical business applications, managing sensitive customer data, or hosting mission-critical services, choosing the right disaster recovery strategy can safeguard your business continuity and minimize the impact of disruption.
When implementing a disaster recovery strategy on AWS, there are two key factors you have to consider. Considering these two factors allows you to align your disaster recovery strategy with your business requirements and define the necessary processes, technologies, and AWS services to achieve the desired recovery objectives. These two factors are Recovery Time Objective and Recovery Point Objective. Let's see what each of them means in brief detail.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) — refers to the maximum tolerable downtime for your applications and services during a disaster. RTO defines the maximum amount of time your applications and services can remain unavailable before it starts impacting your business operations negatively. Think of it as a deadline or a target you set for yourself. For example, if you have an RTO of 4 hours, it means you aim to recover your systems and have them up and running within that time frame. The shorter the RTO, the faster you can bounce back from disruption.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) — This refers to the maximum acceptable data loss that a system can incur in the event of a disaster. If something unexpected happens, the RPO tells you the furthest point you can go back to in terms of saved work. For example, if your RPO is set to 1 hour, it means you can recover your project to a version saved within the past hour. Deciding on the right RPO for your business involves considering factors like how often your data changes, how important it is, and how much you're willing to invest to minimize data loss. Some businesses, like banks or healthcare providers, need very low RPOs to ensure minimal data loss.
Now onto the various disaster recovery strategies that are available on AWS. There are several options to consider based on your specific requirements. Here are some of the common strategies.
Backup and restore
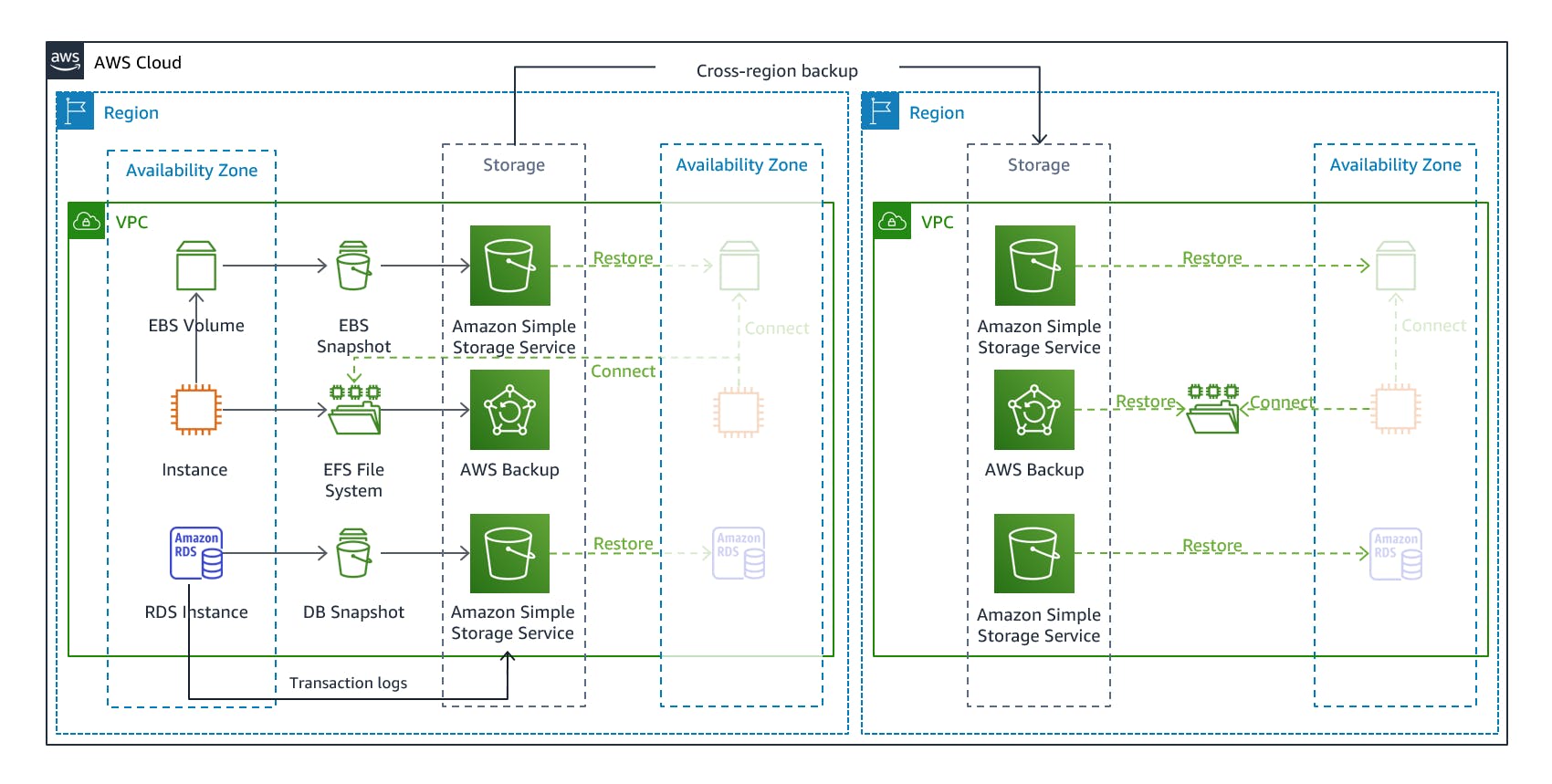
This is a suitable approach for mitigating data loss or corruption. It involves regularly creating backups of your data and applications and storing them in a separate location. This strategy ensures that you have copies of your critical data and systems that can be used for recovery in the event of a disaster or data loss. To implement this strategy on AWS, you can leverage services like Amazon S3 and Glacier. S3 provides highly durable and scalable object storage where you can store your backups. It offers versioning and lifecycle management features that allow you to automate the backup process and retain backups for the required duration. The image below illustrates a sample backup and restore architecture.
Pilot Light
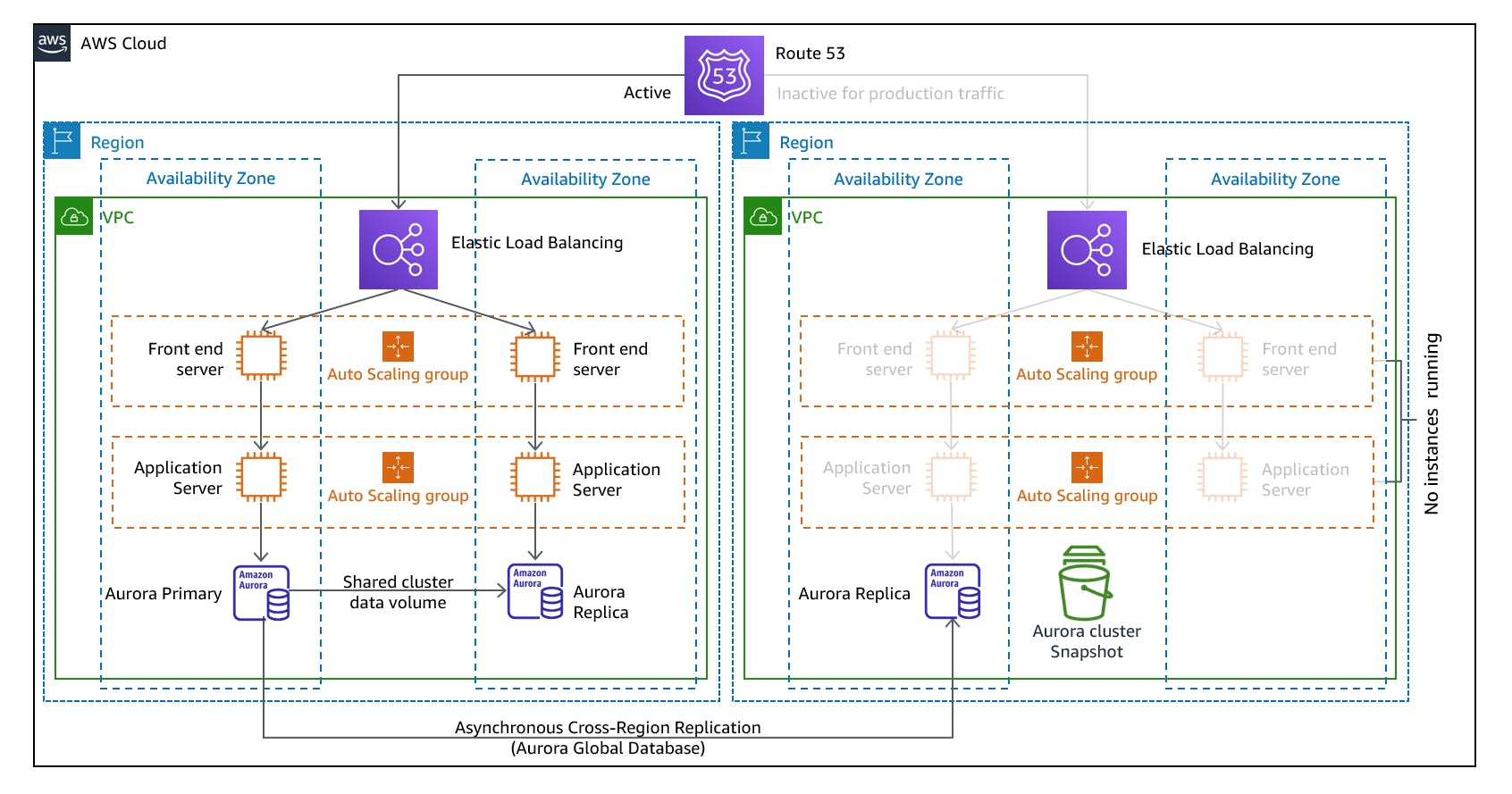
With the pilot light strategy, you have a scaled-down version of your infrastructure running in the cloud. This setup includes only the essential components needed for recovery, such as critical applications, databases, and data storage. The rest of the infrastructure remains idle until a disaster occurs.
One real-world scenario where the Pilot Light strategy is commonly used is in e-commerce businesses. Let's consider an online retail store that experiences high traffic during holiday seasons or special promotions. To ensure uninterrupted service, the retailer can maintain a Pilot Light environment in AWS. This includes a minimal set of web servers, application servers, and a synchronized database. During normal operations, the Pilot Light environment runs at a fraction of the full-scale infrastructure, resulting in lower costs. However, when disaster strikes, the retailer can rapidly scale up the infrastructure by launching additional instances and redirecting traffic to the AWS environment. This allows the retailer to handle the increased load and maintain a seamless customer experience in case of on-premises failures. Pilot Light provides a balance between cost efficiency and high availability, ensuring that critical systems can be quickly restored in the event of a disaster.
Warm Standby
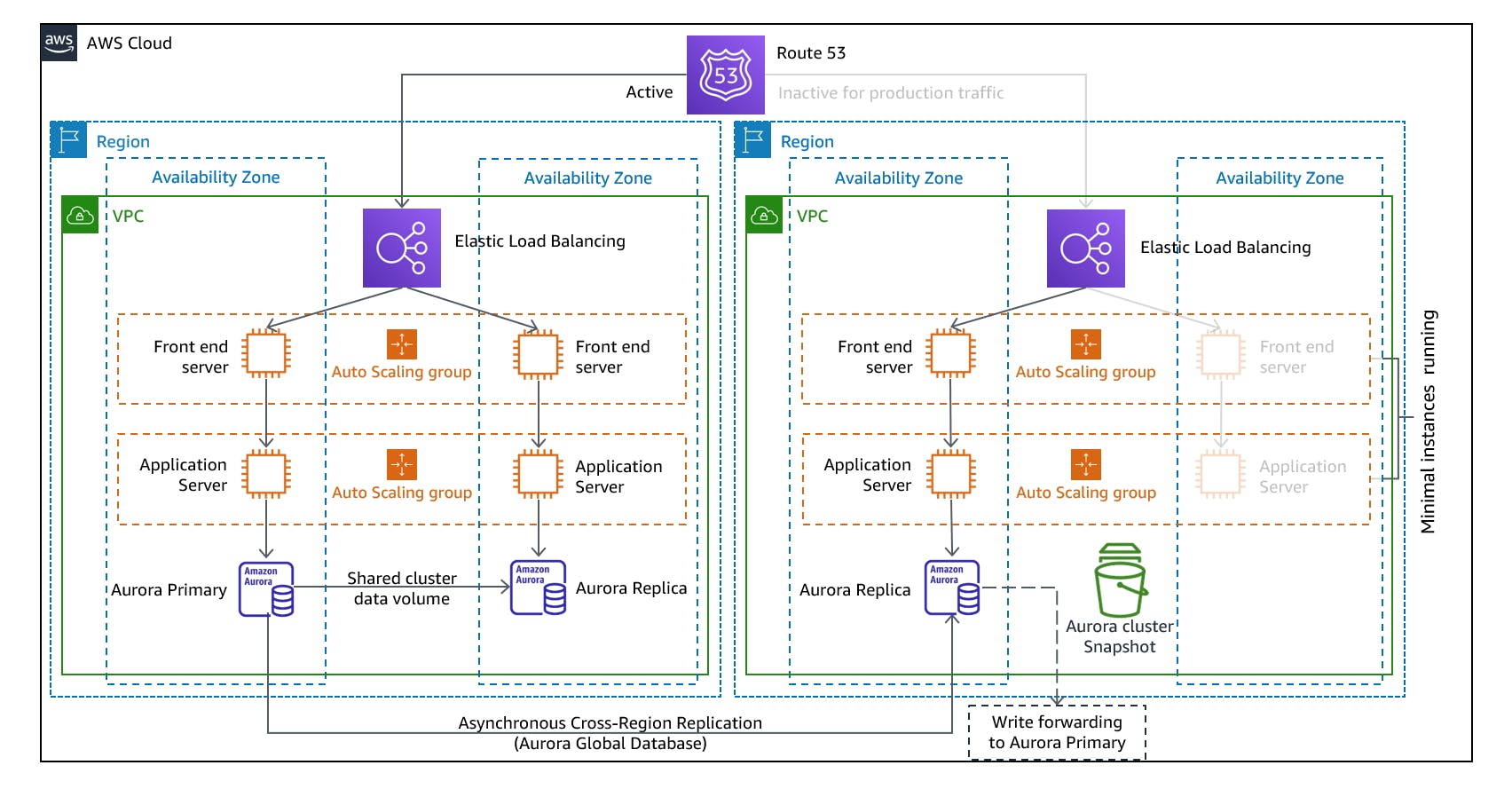
The Warm Standby approach involves maintaining a partially provisioned environment that is ready to take over in case of a disaster. It is a step above the Pilot Light strategy and provides a faster recovery time compared to starting from scratch. In a Warm Standby setup, a subset of infrastructure components is pre-provisioned and running, including virtual machines, databases, and storage. These resources are kept up-to-date and synchronized with the production environment, but they are not actively serving traffic. They act as a warm backup, ready to be activated when needed. When a disaster occurs, the Warm Standby environment can be quickly scaled up by launching additional instances and activating the necessary services. Traffic can be rerouted to the standby environment, allowing it to handle the workload and ensure business continuity.
A real-world scenario where the Warm Standby strategy is commonly used is in financial institutions that require continuous availability of critical systems. For example, a bank's online banking platform may have a Warm Standby environment in AWS. The standby environment would include replicated databases, pre-configured virtual machines, and data storage. In the event of a disaster, such as a data centre outage or hardware failure, the warm standby environment can be activated, ensuring that customers can continue to access their accounts and perform transactions effectively.
Multi Site/Hot Site
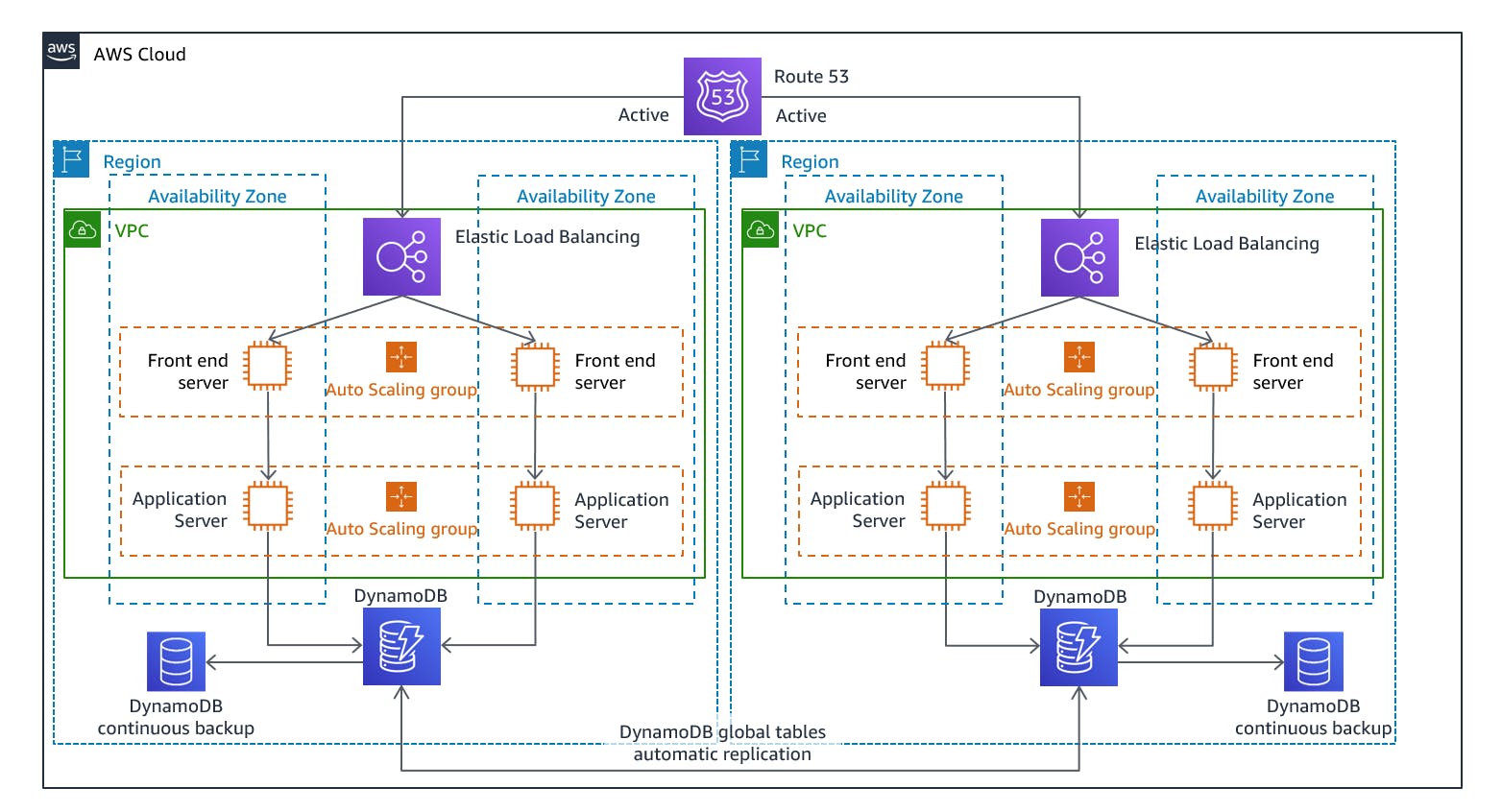
It involves maintaining a fully operational and synchronized replica of an application or infrastructure across multiple AWS regions. It is designed to provide high availability and resilience in the event of a disaster that affects the primary site. In a Multi-Site disaster recovery setup, the application's resources, including servers, databases, storage, and networking, are replicated and deployed across multiple geographically dispersed locations. These locations can be different AWS regions or different AZs within a region. The primary site handles the normal production workload, while the secondary site serves as a standby environment ready to take over in case of a disaster. This disaster recovery strategy offers several benefits, including reduced RTO and RPO, improved application availability, and geographical redundancy. It allows for failover to the secondary site in the event of a disaster, ensuring that business operations can continue with minimal disruption.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right disaster recovery strategy for your solutions built on AWS is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your business's resilience and continuity. By carefully considering factors such as Recovery Time Objective, Recovery Point Objective, cost, complexity and the specific needs of your applications and data, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your business goals. Whether you opt for backup and restore, Pilot Light, Warm Standby, or Multi-Site, remember that no single strategy fits all scenarios. Regular testing, monitoring, and refinement of your disaster recovery plans are essential to ensure their effectiveness. With AWS's robust infrastructure and a well-designed disaster recovery strategy, you can safeguard your business against unforeseen events and minimize disruptions, enabling you to recover quickly and continue serving your customers efficiently.
